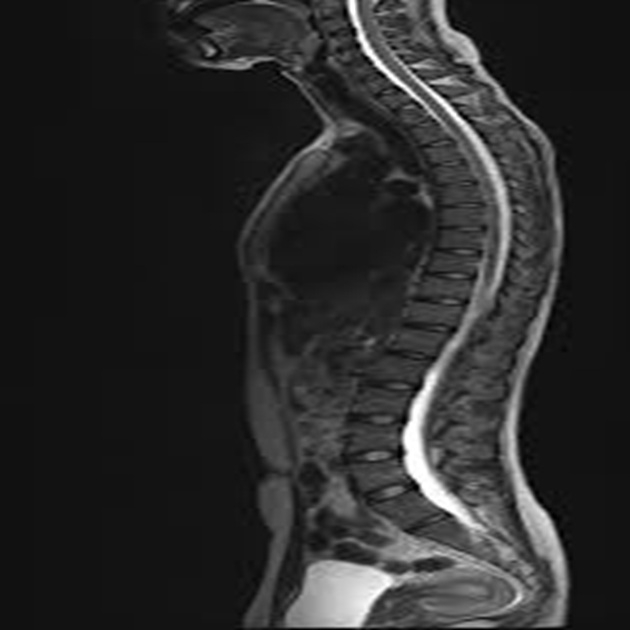
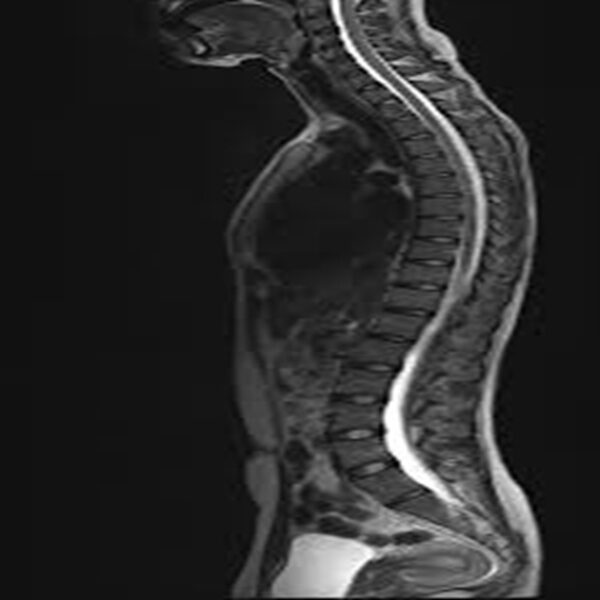
Whole Spine Screening is a comprehensive imaging procedure that evaluates the entire spine, from the cervical region (neck) down to the sacrum (lower back). This type of screening is typically done using X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, depending on the clinical concern. The goal of whole spine screening is to detect abnormalities or conditions that may affect the spine’s bones, soft tissues, and alignment.
X-rays are commonly used for assessing bone structure, alignment, and any signs of fractures, scoliosis, or degenerative changes. CT scans provide detailed cross-sectional images of the bones and can identify more complex fractures or abnormalities. MRI is used to evaluate soft tissues, such as the spinal cord, intervertebral discs, nerve roots, and ligaments, and is particularly helpful in diagnosing conditions like herniated discs, spinal stenosis, tumors, infections, or inflammation.
Whole spine screening is useful for identifying a variety of spine-related issues, including degenerative diseases, congenital abnormalities, infections, tumors, or spinal deformities. It is often recommended for individuals with chronic back pain, unexplained neurological symptoms, or those who are at risk of spinal disorders. The screening helps guide diagnosis and treatment, ensuring comprehensive care for the spine as a whole.






Reviews
Clear filtersThere are no reviews yet.